Learn how to automate Google Drive OCR using n8n and OpenAI to extract document data and store it in Google Sheets with a complete workflow guide.
Handling documents is one of the most time-consuming tasks for businesses, freelancers, and operations teams. Invoices, receipts, scanned forms, and PDFs often arrive in Google Drive, but extracting usable data from them usually requires manual effort. This is slow, error-prone, and difficult to scale.
The n8n Google Drive OCR OpenAI to Google Sheets workflow solves this exact problem. It automates the entire process — from detecting a new file in Google Drive to extracting text using OCR, cleaning and structuring that data with OpenAI, and finally storing it in Google Sheets in a structured format.
This guide explains the workflow in detail, based on real automation patterns used in production systems.
What This Workflow Does
This automation performs five core actions:
- Detects newly uploaded documents in a specific Google Drive folder
- Downloads the document file (PDF or image)
- Extracts text using OCR
- Uses OpenAI to clean, understand, and structure the extracted text
- Saves the final structured data into Google Sheets
The result is a fully automated document-to-data pipeline.
Why Use n8n for Google Drive OCR Automation
n8n is well suited for this type of workflow because it allows flexible logic, data transformation, and API control. Unlike basic automation tools, it supports complex workflows that involve file handling, AI processing, and structured outputs.
Key reasons n8n is effective here:
- Visual workflow design with advanced logic
- Direct integration with Google Drive and Google Sheets
- Ability to connect OCR services and OpenAI
- Self-hosting option for data control
- Error handling and retries for production reliability
This makes it possible to build a stable OCR + AI system without writing full applications.
Real-World Use Cases
This workflow is not theoretical. It is commonly used for:
- Invoice data extraction (invoice number, date, total, vendor)
- Expense receipt processing
- Client document intake automation
- Digitizing scanned PDFs into structured records
- Creating searchable document databases
- Reducing manual data entry for finance and operations teams
The search intent behind this keyword comes from users actively trying to implement these systems.
Workflow Architecture Overview
Before going step by step, it is important to understand the structure:
- Trigger: Google Drive file upload
- File Handling: Download document as binary
- Text Extraction: OCR processing
- AI Processing: OpenAI cleanup and structuring
- Storage: Google Sheets row insertion
Each stage addresses a specific technical requirement and is necessary for reliability.
Step 1: Google Drive Trigger Configuration

The workflow starts with a Google Drive trigger node.
Best practices:
- Monitor a dedicated folder, not the entire Drive
- Trigger on “File Created”
- Avoid folders with frequent non-document uploads
Using a dedicated folder ensures the automation runs only when relevant files are added and avoids unnecessary executions.
Step 2: Download the File from Google Drive
Google Drive triggers provide metadata, not the file itself.
A download step is required to retrieve the actual document.
Important points:
- Preserve original file format
- Ensure binary data is passed correctly to the OCR step
- Handle large files carefully to avoid memory issues
This step ensures the OCR engine receives the correct input.
Step 3: OCR Text Extraction
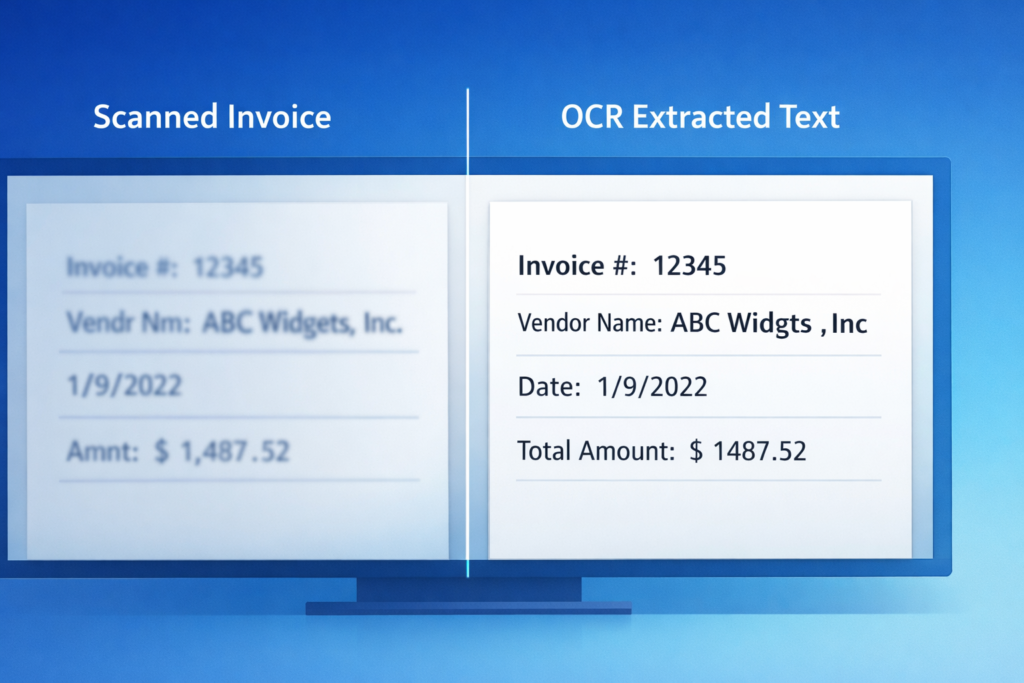
OCR converts images and scanned PDFs into machine-readable text.
Common OCR inputs:
- Scanned invoices
- Image-based PDFs
- JPG, PNG, or TIFF files
OCR output is usually:
- Unstructured
- Noisy
- Inconsistent across documents
This is expected and is not a failure of the workflow. OCR accuracy depends on scan quality, document layout, and language clarity.
Step 4: Processing OCR Output with OpenAI
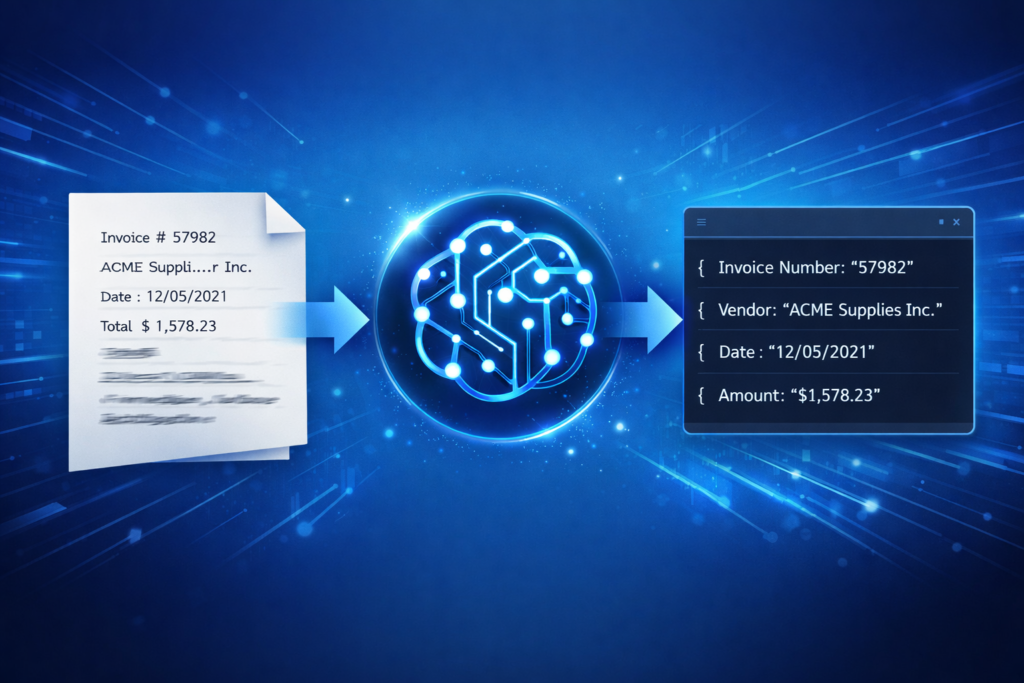
OCR alone is not enough. The extracted text often contains errors, broken formatting, and irrelevant data.
This is where OpenAI is used to:
- Correct OCR mistakes
- Identify relevant fields
- Convert text into structured data
- Apply contextual understanding
The OpenAI step is designed to transform raw OCR text into a clean, structured format suitable for storage and analysis.
Typical structured outputs include:
- Invoice number
- Vendor name
- Date
- Amount
- Currency
- Document type
This step replaces manual parsing logic with AI-based understanding.
Step 5: Data Validation and Normalization
Before storing data, validation is critical.
Common checks include:
- Ensuring required fields exist
- Normalizing date formats
- Converting numbers from text
- Handling missing or unclear values
In n8n, this is done using logic and data transformation nodes.
This prevents incorrect or incomplete data from entering Google Sheets.
Step 6: Save Data to Google Sheets
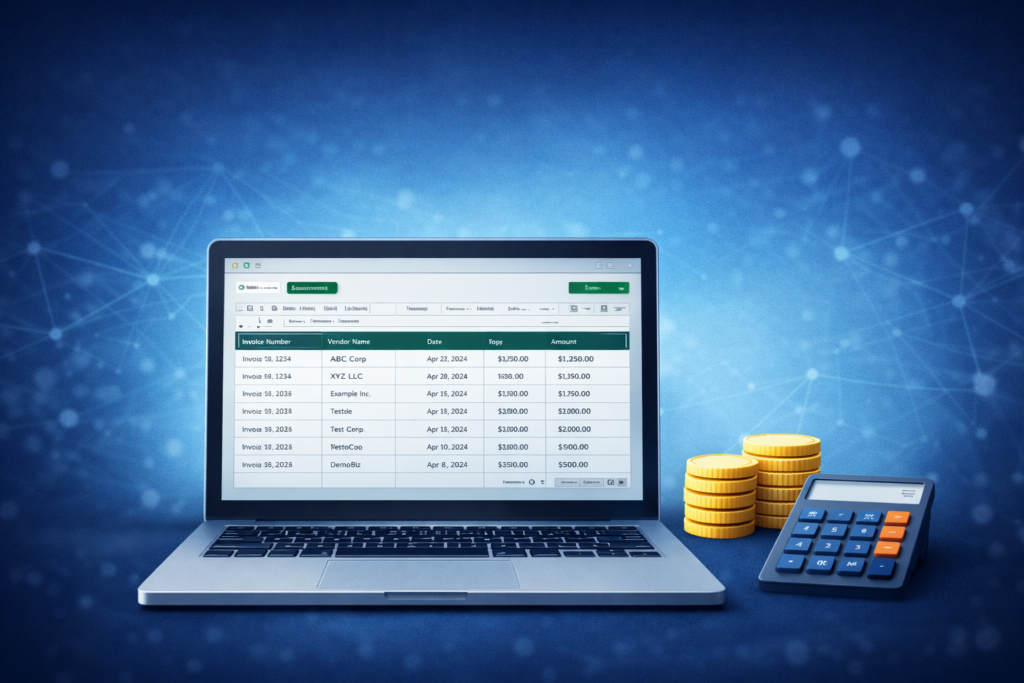

Once the data is structured and validated, it is stored in Google Sheets.
Best practices:
- Predefine column headers
- Match AI output keys exactly
- Store raw OCR text in a separate column if auditing is needed
Google Sheets becomes a live database that can be filtered, shared, or connected to other systems.
Error Handling and Reliability
Production workflows must handle failures gracefully.
Common failure points:
- OCR API timeouts
- OpenAI response inconsistencies
- Invalid file formats
- Network interruptions
To improve reliability:
- Add error workflows
- Log failed files
- Use retries for temporary failures
- Separate OCR and AI processing if needed
These practices are essential for real-world use.
Security and Data Privacy
Document automation often involves sensitive information.
Important considerations:
- Restrict access to the monitored Drive folder
- Secure API keys using environment variables
- Avoid sending unnecessary data to OpenAI
- Self-host n8n when compliance is required
Security is part of workflow design, not an optional feature.
Performance and Scaling
As document volume increases, performance optimization becomes necessary.
Scaling strategies:
- Batch processing
- File archiving after processing
- Splitting workflows into stages
- Using queues or delays
This prevents API rate limits and keeps the system stable under load.
Who Should Use This Workflow
This automation is ideal for:
- Freelancers offering automation services
- Small businesses managing financial documents
- Agencies handling client data pipelines
- SaaS builders creating document processing systems
- Operations teams reducing manual workload
It is designed for real usage, not demos.
Conclusion
The n8n Google Drive OCR OpenAI to Google Sheets workflow is a practical, scalable solution for automating document processing. It replaces manual data entry with a reliable automation pipeline that extracts, cleans, and stores information with minimal human intervention.
This workflow is not about trends or hype. It addresses a real operational need using tools that are already widely adopted.
By implementing this system, businesses gain efficiency, accuracy, and scalability — while maintaining control over their data and processes.